People nowadays have access to a massive amount of video via the internet. The number of videos from which a viewer may pick is staggering. As a result, it is impossible for viewers to sift through a large number of films to select one that they are interested in. On the internet, images and videos have gone worldwide, encouraging individuals to design algorithms that integrate semantic content for a variety of applications. For a better categorization result, it also contains video search and optimization. One way for viewers to narrow down their options is to search for videos within certain categories. Because of the large number of videos to categorize, work on Large-Scale Video Classification has begun.
We reviewed video classification datasets and some fundamental algorithms for this problem in the previous blog. One of the most common approaches is to use a recurrent neural network (RNN) to solve the problem of remembering the state of prior frames while analyzing frame.
A Review about Recurrent Neural Network
Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) has recently been identified as a useful class of models for comprehending picture material. It provides state-of-the-art picture recognition, segmentation, detection, and retrieval results. The literature review of the various techniques used for video classification is discussed here, and all techniques are compared against each other based on factors such as the video classification algorithm used in each approach, the model for classification, and the features extracted for classification in each technique. Finally, it is determined if each approach is capable of dealing with both time and spatial complexity and whether each technique is suited for managing large size datasets. We investigated the effectiveness of RNNs in large-scale video classification and presented a model to handle the video classification with visual feature extraction such as color and texture, inspired by favorable results in image and speech recognition.
A recurrent neural network (RNN) is a type of artificial neural network in which unit connections form a directed loop. This cycle causes the network's internal state to change, allowing it to display dynamic temporal behavior. RNNs may process arbitrary input sequences using their internal memory. As a result, they may be used for tasks like unsegmented connected handwriting recognition, which has the greatest results.
In the traditional neural networks, models recive a fixed-sized vector as input (e.g. an image) and produce a fixed-sized vector as output (e.g. probabilities of different classes). Not only that: These models perform this mapping using a fixed amount of computational steps (e.g. the number of layers in the model). The core reason that recurrent nets are more exciting is that they allow us to operate over sequences of vectors: Sequences in the input, the output, or in the most general case both.
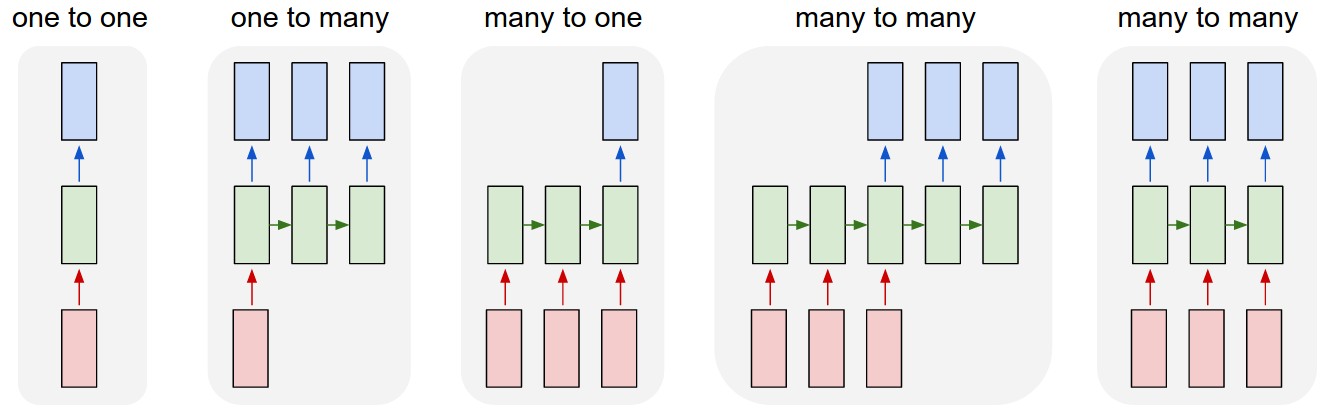
Figure 1 shows some cases of RNN. The arrows denote functions, and each rectangle represents a vector (e.g. matrix multiply). The input vectors are red, the output vectors are blue, and the RNN's state is held by green vectors (more on this soon). 1. Non-RNN, vanilla manner of processing, from fixed-sized input to fixed-sized output (e.g. image classification). 2. A variety of outputs, such as a sequence (e.g. image captioning takes an image and outputs a sentence of words). 3. A variety of inputs, such as a sequence (e.g. sentiment analysis where a given sentence is classified as expressing positive or negative sentiment). 4. Sequence input and sequence output (e.g. Machine Translation: an RNN reads a sentence in English and then outputs a sentence in French). 5. Input and output sequences that are in sync (e.g. video classification where we wish to label each frame of the video)
Applying LSTM for Video Classification
The work is using LSTM to train sport dataset with SIFT feature. Figure 2 illustrates the basic framework of the proposed approach.
- The goal is to categorize soccer video sequences using a set of descriptors (one descriptor per picture) that relate to a set of features.
- The selection of such features is critical to the classification's success.
- Based on the temporal evolution of the descriptors, a Recurrent Neural Network (RNN) including Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) neurons is trained to categorize each action type.
- To do this, descriptors (one per timestep) are provided to the neural network, which then makes a final decision based on the aggregation of multiple individual decisions.